Semantic Image Synthesis with Spatially-Adaptive Normalization
Semantic Image Synthesis with Spatially-Adaptive Normalization Taesung Park, Ming-Yu Liu, Ting-Chun Wang, Jun-Yan Zhu. CVPR 2019(oral)
-
semantic image synthsis 指出了论文对应的任务, 也就是将semantic map转换为realistic images.
-
spatially-adaptive normliazation 指出了论文的contribution, spatially-adaptive 表示对不同location进行不同的处理.
论文评价: 简单的思路, 优秀的效果, 中规中矩的实验分析.
1. Previous Work
-
Semantic Image Synthesis:
-
Pix2pix
-
Pix2pixHD
-
-
Style Transfer:
-
TODO: style transfer中的normalization进行affine transform吗?(例如fast style transfer)
-
之前工作的问题:
-
无法生成multi-modal的结果
-
semantic map的信息在upsample过程中容易丢失, normalization layers会 wash away semantic information.
2. Motivation
Spatially Adaptive意味着每个location可以进行不同的transform, 不同于batch-norm, instance-norm等对整个channel进行相同的normalization(和transform).
Motivation来源(推测): . StyleGAN . Conditional normalization .. TODO
3. Method
3.1. Spatially-adaptive denormalization
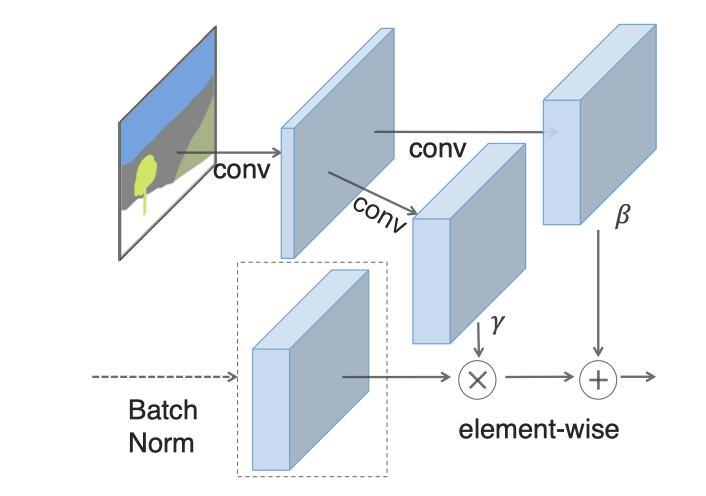
-
SPADE的由来: SPatially-Adaptive (DE)normalization
-
为什么叫做denormalization? : conditional batchnormalization会利用external data对normalized actiavtions进行denormalize, denormalization本身是conditional.
-
如何实现?
-
normalizatoin
经典的convolution中的batchnorm, 对于
NCHW的一个batch, 求C个N*H*W的tensor的mean和variance, 并进行normalization -
spatial-adaptive affine transformation:
根据不同scale大小的semantic map求出大小为
CHW的\$\gamma\$和\$\beta\$, 然后进行乘法和加法操作
-
-
与(Conditional) Batchnorm的联系
-
normalization过程相同
-
但与batch-norm不同的是, affine transformation是会对不同location求出不同的参数
-
-
与AdaIN(Adaptive Instance Normalization)的联系
把mask替换为style image, 变为spatially-invariant, 设置N=1, 就得到了AdaIN
3.2. Why does the SPADE work better?
-
如果一个semantic map在不同位置的值都相同, 那么传统pix2pixHD在conv之后得到的tensor的值在各个位置也相同, instance norm之后, 得到的值都变为0. 对于semantic map这种uniform分布较多的情景, 容易丢失semantic map的信息.
-
对于SPADE, normalization的是activation, 而最初的输入时表示style的tensor(不会想semantic map一样uniform分布), 因此SPADE能更好的保留semantic information.
3.3. Multi-modal Synthesis
问题: 类似的分离style的multi-modal synthesis的范式和原理是什么? TODO . pix2pix HD . multi-modal I2I . starGAN
4. Implementation
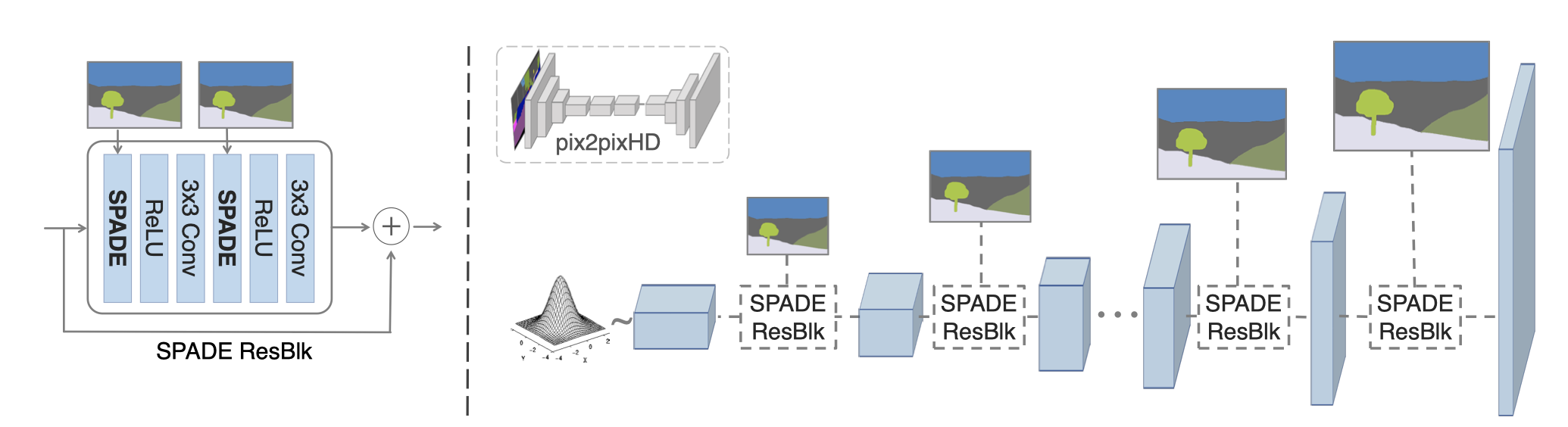
4.1. Model
4.1.1. Generator
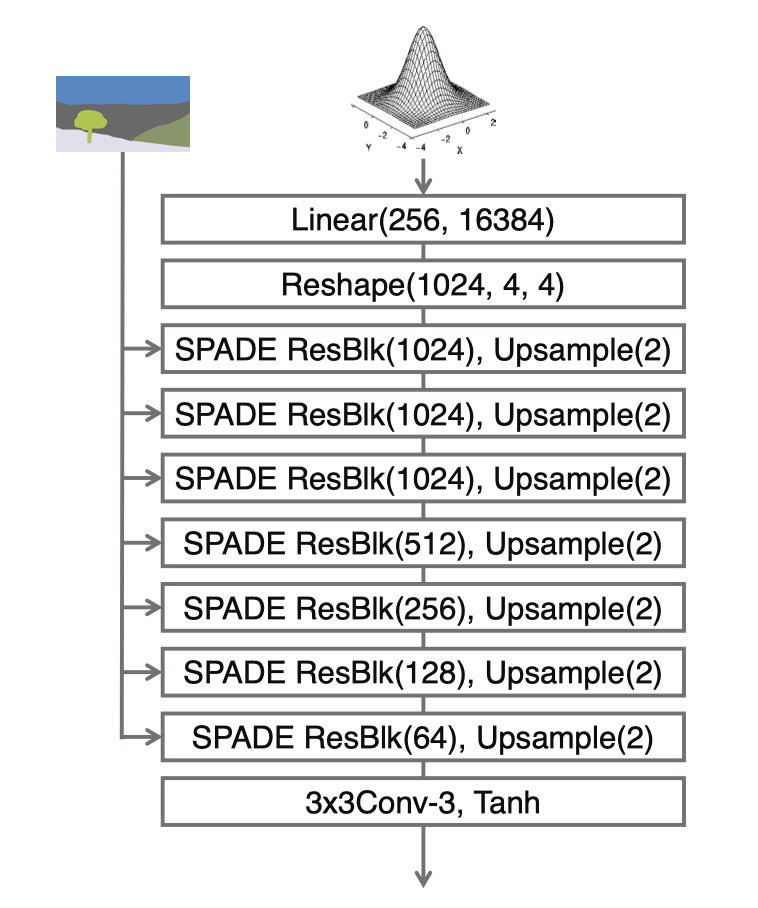
-
输入为latent vector和semantic map
-
generator为SPADEResnetBlock和Upsample层的交替叠加
upsample替代transpose-convolution的工作越来越多, 这样可以减少artifact的产生
class SPADEGenerator(BaseNetwork):
@staticmethod
def modify_commandline_options(parser, is_train):
parser.set_defaults(norm_G='spectralspadesyncbatch3x3')
parser.add_argument('--num_upsampling_layers',
choices=('normal', 'more', 'most'), default='normal',
help="If 'more', adds upsampling layer between the two middle resnet blocks. If 'most', also add one more upsampling + resnet layer at the end of the generator")
return parser
def __init__(self, opt):
super().__init__()
self.opt = opt
nf = opt.ngf
self.sw, self.sh = self.compute_latent_vector_size(opt) (1)
if opt.use_vae:
# In case of VAE, we will sample from random z vector
self.fc = nn.Linear(opt.z_dim, 16 * nf * self.sw * self.sh) (2)
else:
# Otherwise, we make the network deterministic by starting with
# downsampled segmentation map instead of random z
self.fc = nn.Conv2d(self.opt.semantic_nc, 16 * nf, 3, padding=1) (2)
self.head_0 = SPADEResnetBlock(16 * nf, 16 * nf, opt)
self.G_middle_0 = SPADEResnetBlock(16 * nf, 16 * nf, opt)
self.G_middle_1 = SPADEResnetBlock(16 * nf, 16 * nf, opt)
self.up_0 = SPADEResnetBlock(16 * nf, 8 * nf, opt)
self.up_1 = SPADEResnetBlock(8 * nf, 4 * nf, opt)
self.up_2 = SPADEResnetBlock(4 * nf, 2 * nf, opt)
self.up_3 = SPADEResnetBlock(2 * nf, 1 * nf, opt)
final_nc = nf
if opt.num_upsampling_layers == 'most':
self.up_4 = SPADEResnetBlock(1 * nf, nf // 2, opt)
final_nc = nf // 2
self.conv_img = nn.Conv2d(final_nc, 3, 3, padding=1)
self.up = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2)
def compute_latent_vector_size(self, opt):
if opt.num_upsampling_layers == 'normal':
num_up_layers = 5
elif opt.num_upsampling_layers == 'more':
num_up_layers = 6
elif opt.num_upsampling_layers == 'most':
num_up_layers = 7
else:
raise ValueError('opt.num_upsampling_layers [%s] not recognized' %
opt.num_upsampling_layers)
sw = opt.crop_size // (2**num_up_layers)
sh = round(sw / opt.aspect_ratio)
return sw, sh
def forward(self, input, z=None):
seg = input
if self.opt.use_vae:
# we sample z from unit normal and reshape the tensor
if z is None:
z = torch.randn(input.size(0), self.opt.z_dim,
dtype=torch.float32, device=input.get_device())
x = self.fc(z)
x = x.view(-1, 16 * self.opt.ngf, self.sh, self.sw)
else:
# we downsample segmap and run convolution
x = F.interpolate(seg, size=(self.sh, self.sw))
x = self.fc(x)
x = self.head_0(x, seg)
x = self.up(x)
x = self.G_middle_0(x, seg)
if self.opt.num_upsampling_layers == 'more' or \
self.opt.num_upsampling_layers == 'most':
x = self.up(x)
x = self.G_middle_1(x, seg)
x = self.up(x)
x = self.up_0(x, seg)
x = self.up(x)
x = self.up_1(x, seg)
x = self.up(x)
x = self.up_2(x, seg)
x = self.up(x)
x = self.up_3(x, seg)
if self.opt.num_upsampling_layers == 'most':
x = self.up(x)
x = self.up_4(x, seg)
x = self.conv_img(F.leaky_relu(x, 2e-1))
x = F.tanh(x)
return x-
latent vector size是根据什么计算的? 在图像大小的基础上, 每个upsample layer, 将width除2, height根据aspect ratio决定
-
16对应的是什么? last conv layer和first conv layer的channel个数的倍数是16, nf是最后一个conv层的filter数量
4.2. SPADEResBlock
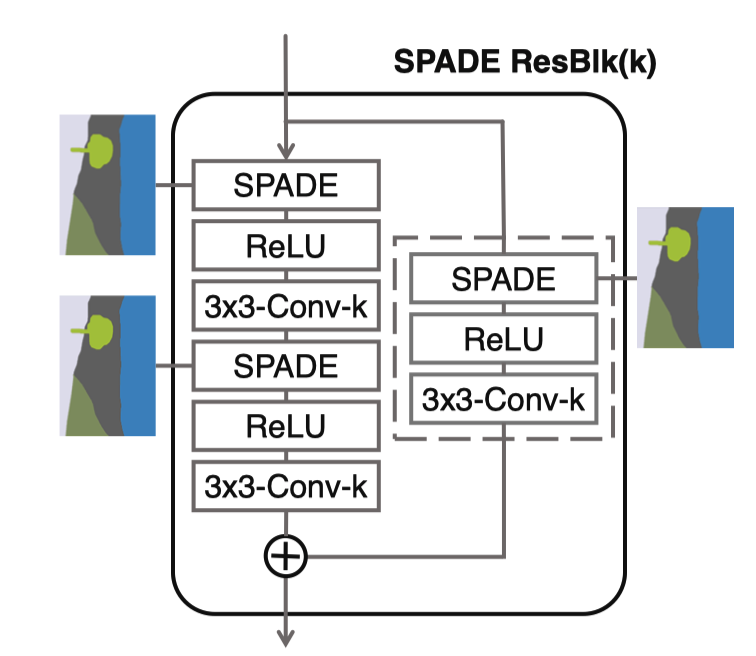
-
与传统ResBlock相似, 2个Conv加上skip-connection
-
learned skip connection来自于参考文献3
-
每个Conv层使用 spectral normalization
-
为什么resblock最后不加ReLU呢? TODO
class SPADEResnetBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, fin, fout, opt):
super().__init__()
# Attributes
self.learned_shortcut = (fin != fout)
fmiddle = min(fin, fout)
# create conv layers
self.conv_0 = nn.Conv2d(fin, fmiddle, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.conv_1 = nn.Conv2d(fmiddle, fout, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
if self.learned_shortcut:
self.conv_s = nn.Conv2d(fin, fout, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
# apply spectral norm if specified
if 'spectral' in opt.norm_G:
self.conv_0 = spectral_norm(self.conv_0)
self.conv_1 = spectral_norm(self.conv_1)
if self.learned_shortcut:
self.conv_s = spectral_norm(self.conv_s)
# define normalization layers
spade_config_str = opt.norm_G.replace('spectral', '')
self.norm_0 = SPADE(spade_config_str, fin, opt.semantic_nc)
self.norm_1 = SPADE(spade_config_str, fmiddle, opt.semantic_nc)
if self.learned_shortcut:
self.norm_s = SPADE(spade_config_str, fin, opt.semantic_nc)
# note the resnet block with SPADE also takes in |seg|,
# the semantic segmentation map as input
def forward(self, x, seg):
x_s = self.shortcut(x, seg)
dx = self.conv_0(self.actvn(self.norm_0(x, seg)))
dx = self.conv_1(self.actvn(self.norm_1(dx, seg)))
out = x_s + dx
return out
def shortcut(self, x, seg):
if self.learned_shortcut:
x_s = self.conv_s(self.norm_s(x, seg))
else:
x_s = x
return x_s
def actvn(self, x):
return F.leaky_relu(x, 2e-1)4.3. SPADE实现
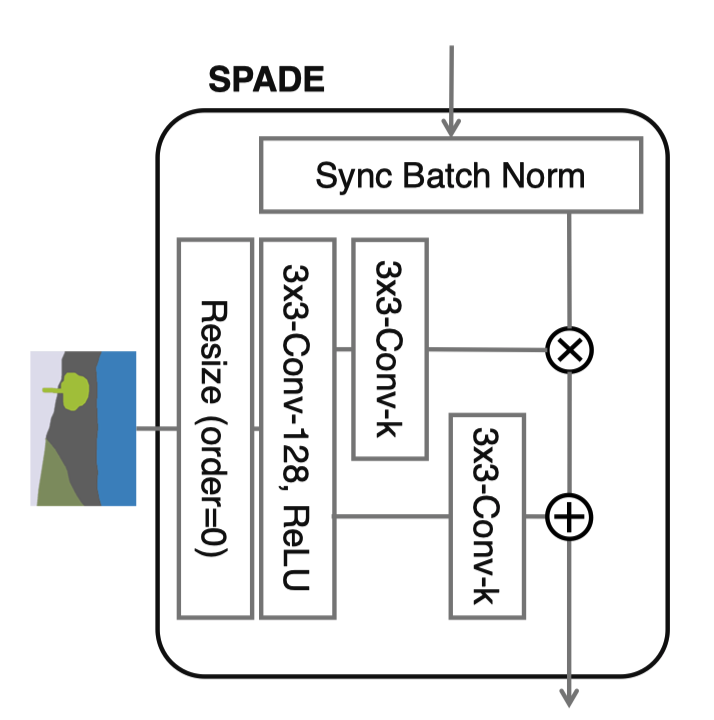
-
segment map的shape怎么和activation对齐? nearest-neighbour下采样 (order=0, order为1是线性插值)
-
Sync Batch Norm是干什么的? Pytorch中
nn.DataParallel在多个GPU下训练时分别使用单个device的statistics进行normalize(这样会更快), sync batch norm实现使用所有device中的数据来求statistics, 参考链接
class SPADE(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config_text, norm_nc, label_nc):
super().__init__()
assert config_text.startswith('spade')
parsed = re.search('spade(\D+)(\d)x\d', config_text)
param_free_norm_type = str(parsed.group(1))
ks = int(parsed.group(2))
if param_free_norm_type == 'instance':
self.param_free_norm = nn.InstanceNorm2d(norm_nc, affine=False)
elif param_free_norm_type == 'syncbatch':
self.param_free_norm = SynchronizedBatchNorm2d(norm_nc, affine=False)
elif param_free_norm_type == 'batch':
self.param_free_norm = nn.BatchNorm2d(norm_nc, affine=False)
else:
raise ValueError('%s is not a recognized param-free norm type in SPADE'
% param_free_norm_type)
# The dimension of the intermediate embedding space. Yes, hardcoded.
nhidden = 128
pw = ks // 2
self.mlp_shared = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(label_nc, nhidden, kernel_size=ks, padding=pw),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.mlp_gamma = nn.Conv2d(nhidden, norm_nc, kernel_size=ks, padding=pw)
self.mlp_beta = nn.Conv2d(nhidden, norm_nc, kernel_size=ks, padding=pw)
def forward(self, x, segmap):
# Part 1. generate parameter-free normalized activations
normalized = self.param_free_norm(x)
# Part 2. produce scaling and bias conditioned on semantic map
segmap = F.interpolate(segmap, size=x.size()[2:], mode='nearest') (1)
actv = self.mlp_shared(segmap)
gamma = self.mlp_gamma(actv)
beta = self.mlp_beta(actv)
# apply scale and bias
out = normalized * (1 + gamma) + beta
return out-
interpolate使得semantic map和x的长宽相同
4.4. Discriminator
采用pix2pixHD的设计结构
4.5. Objective
-
GAN loss: hinge loss
-
Feature Mathching Loss
-
VGG perceptual loss
4.6. 代码技巧
-
options的结构
-
find module by name
5. Experiment
5.1. 对比工作
-
pix2pixHD
-
CRN
-
SIMS
5.2. Ablation Study
5.2.1. Effectivenss of the SPADE
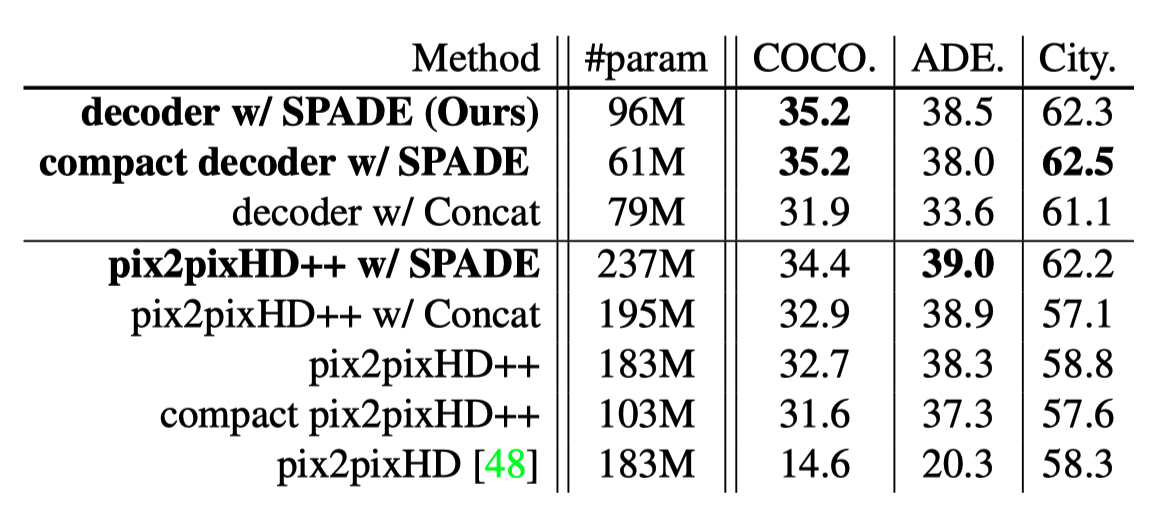
5.2.2. Variations of SPADE
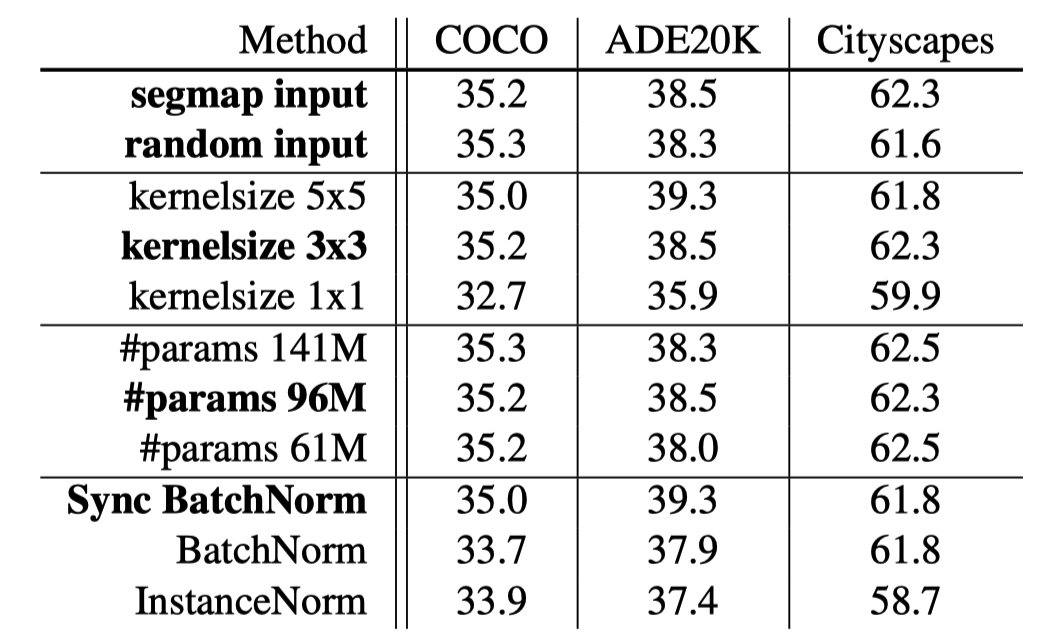
-
输入noise还是segmap: 区别不大,说明了SPADE可以有效嵌入semantic map的信息
-
生成\$\alpha, \beta\$ 时用的conv的kernel size: 1x1的时候效果较差,说明
-
normalization type: 影响不大
-
generator中filters数量导致的params的个数: 参数量的提高不一定会带来明显的性能提升
6. Reference Paper
-
A learned representation for artistic style. 2017 (conditional batchnorm)
-
Modulating early visual processing by language. 2017
-
Which Training Methods for GANs do actually Converge? 2018 (ResBlock)
-
Geometric GAN(hinge loss)
7. 单词时间
-
seminal: strongly influencing later developments; 开创性的
Seminal work computes the output image by stitching pieces from a single image (e.g., Image Analogies [16]) or using an image collection [7, 14, 23, 30, 35]
-
modulate: exert a modifying or controlling influence on; 调制(信号学术语)
To address the issue, we propose spatially-adaptive normalization, a conditional normalization layer that modulates the activations using input semantic layouts through a spatiallyadaptive, learned transformation and can effectively propagate the semantic information throughout the network.